Cell therapy has been developing for the last 30 years and it shows results in the treatment of such pathologies as diabetes, multiple sclerosis, encephalopathies, rheumatic diseases, cardiomyopathy, conditions after a heart attack or stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Alzheimer’s disease, myasthenia gravis, Crohn’s disease, autism, cirrhosis, and many others. Сell products are also used in rejuvenation programs.
At Global Power LLC, we use autologous (own) and allogeneic (donated) mesenchymal stromal cells, stem cell exosomes, and stromal vascular fraction. The most commonly used cell product is based on multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MMSCs). As a cell treatment product MMSCs can be transplanted intravenously, intramuscular, via inhalation, into the spinal canal or directly into the damaged area.
Applying only stem cells in some cases may be not enough. Cell therapy works more effectively when combined with other therapeutic methods (detoxification, xenon gas, SWT, etc.) that help decrease inflammation, restore mobility, and activate the tissue repair process.
You might have heard about the treatment of diseases with bone marrow transplantation. Today, bone marrow is not the only source of cells for therapy. Cell material is harvested from peripheral blood, adipose tissue, skin, also placenta and umbilical cord taken after a healthy birth.
In this article, we are going to tell you about stem cell therapy, how effective it is and how the procedure is carried out.
How do stem cells work?
In high concentration transplanted MMSCs enhance the survival and renewal of healthy tissue cells by activating the differentiation of local stem cells, which helps to restore lost tissue functions. Stem cells also have immunomodulatory effects and the ability to stimulate the development of neurons as well as new blood vessels.
In the therapy, when stem cells are introduced into a patient’s body, they circulate in the blood system until they are attracted to proteins secreted around inflamed or damaged tissue. Stem cells then rush to that injured area and start producing various growth factors, chemokines (help cells to migrate), and adhesion molecules (regulate cell interactions at the molecular level).
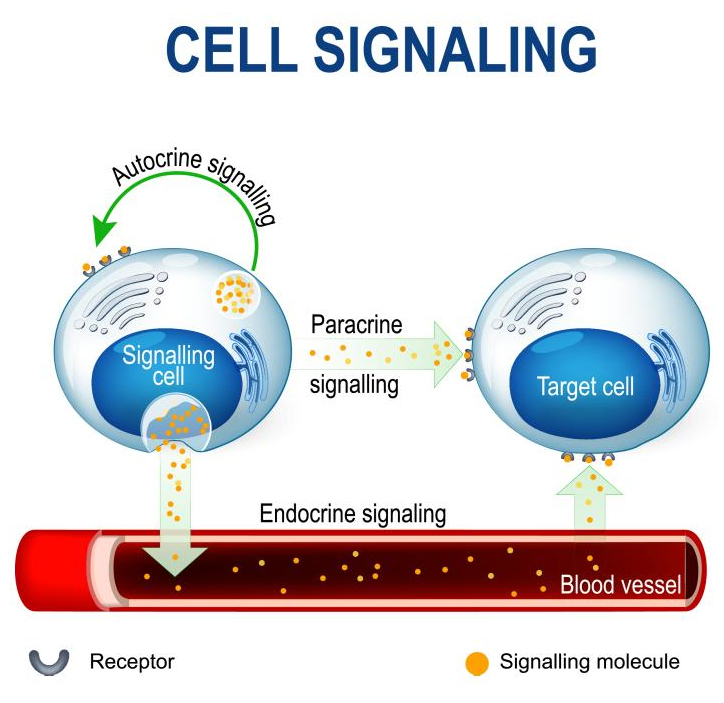
The main therapeutic effect of stem cells is their ability to produce cytokines and growth factors in the intercellular space. These special chemicals are able to activate the regenerative functions of distant cells and promote tissue recovery. This mechanism is called paracrine regulation. Cytokines help block the signals of inflammation in various diseases, including autoimmune processes. An important feature of these signal molecules is that their concentrations may be regulated by inflammation and strictly depend on the stage of tissue regeneration.
Using cell products based on stromal cells we can boost the production of cytokines, leading to improved function of the damaged tissue.
What therapeutic effects are expected?
At Global Power LLC, with the helpful properties of cell therapy, we can treat and achieve improvement of diseases of the nervous system, musculoskeletal system, heart, digestive organs, autoimmune system, as well as issues related to age, genetic diseases, and more.
Here are some results of our patients
Marino, from Melbourne, Australia, 41 years old. He was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. He had problems with balance, vision, and feeling in his hands. Medicines were not working. After he had stem cell treatment he felt more energetic, his vision improved, and his General state “is getting better and better”.
Celeste from the USA. Diabetes type 1. Two years ago she underwent treatment with stem cells harvested from her own bone marrow. This gave an increase in her C-peptide level that almost doubled from 0.03 up to <0.05. This indicator shows the level of natural insulin production. After the second therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells, the level of C-peptide rose from 1.15 to 1.9. This means that the patient’s body began to produce its own insulin even after 22 years of illness!
A patient from London brought his 77-year-old mother to Global Power LLC for treatment. She suffered from pain in her legs and heart disease. Therapy with stem cells taken from donated umbilical cord blood was applied. Now the patient says she feels stronger and walks better, and the pain in her joints has been alleviated.
Get a free online consultation
Please, contact our medical advisor to discuss your health condition with a specialist in regenerative medicine. You can also leave your contact details for a callback. It is free and confidential.
Types of cell products for stem cell therapy
Depending on the therapeutic purposes, different cell-based products can be used for different tasks. The doctor will recommend options, which are likely to work in your case. All of our cell products are prepared and cultivated in our own laboratory.

SVF – stromal vascular fraction. SFV contains various stem and progenitor cells, including MMSCs, as well as immune cells (monocytes and macrophages), fibroblasts, pericytes, endothelial progenitor cells and other types of helpful cells that are involved in the regeneration process. For example, tissue-specific progenitor cells are presented in various tissues of the body, they replace the dead cells, thus contributing to the renewal of the cell population and, as a result, to tissue regeneration.
SFV can be isolated from lipoaspirate and used as a rapid and safe method for facilitating the healing of chronic wounds, treatment of osteoarthritis, systemic and multiple sclerosis, heart disease, allergy, alopecia, etc.
Harvesting adipose-derived stem cells is a much easier procedure than a bone marrow extraction. Lipoaspirate also contains much larger volumes (x2500) of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells with higher growth capacity and a lower ageing rate than stromal cells sourced from bone marrow.
Cultivated MMSCs – multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Due to their ability to activate the recovery of damaged tissues, they are used in the treatment of a large number of pathologies, including neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, arthritis and arthrosis, digestive system disorders, arterial hypertension and infarction, pulmonary diseases, obesity, erectile dysfunction, in the recovery after injuries, etc.
Fibroblasts – dermal cells that are responsible for the skin’s ability to repair and renew. The function of fibroblasts is to produce collagen, elastin, and hyaluronic acid. It’s used in programs designed to correct the external signs of ageing.
Other types of cell products. In some cases, stem cells-derived exosomes, hematopoietic stromal cells isolated from the blood of the umbilical cord (treatment of blood diseases), regulatory T-cells (in autoimmune diseases treatment), dendritic cell vaccines and bone marrow mononuclear cells (MNC) can be used.
Own and donated stem cells for the therapy
Based on their source, stem cells for treatment are divided into two categories:
- Autologous (donor and recipient are the same) – can be obtained from the patient’s own tissues (adipose tissue, bone marrow, peripheral blood, skin, gingiva).
- Allogeneic (donor is not the patient) – can be obtained from donated tissues (all of the above + placenta and umbilical cord harvested only with the consent of the donor and only as a result of healthy birth).

To achieve the best therapeutic effect, we prescribe donor cells in situations:
- If there are contraindications to anesthesia or a high risk of bleeding in a sampling of the patient’s own biomaterial. When using cell products from donated tissues there is no need to perform an invasive procedure such as adipose-tissue aspiration or bone marrow extraction.
- If the patient’s cells have a low proliferative potential (the ability to reproduce).
- If therapy should be started immediately. There is no need to deliver samples to an outside laboratory and wait days for the cells to be returned for injection – donated cells have already been harvested and are available.
MMSCs do not produce specific proteins that are recognized by the immune system, so they remain “invisible”. Regardless of the source from which they were harvested, stem cells are highly biocompatible and there is no risk of rejection.
Transplantation of MMSCs. How is the procedure carried out?
First, the patient undergoes a full examination to determine the current state of health. Then our specialist makes a conclusion about the appropriateness and expected effects of therapy.
Next, the question is whether self-sourced or donor stem cells will be used. In the first case, the biopsy is performed and stromal cells are isolated from the patient’s own biomaterial. Then the harvested cells are cultivated to the required volume. Usually, this takes 3-4 weeks depending on the proliferative potential of the MMSCs. After that, the cultivated cells can be used for therapy or stored in a cryobank for an unlimited period of time. In the case of donor cells, the cell product can be used immediately in the initial treatment.
The use of cell products is carried out under medical supervision. The volume of cell mass required for treatment is calculated depending on the patient’s body weight. Before use, a test for sterility and infectious/bacteriological safety is carried out. Then a passport of the cell product is drawn up. This passport indicates the name of the cell product, the source of cells, the date of extraction, cell characteristics, description of final product formulation, etc.
Routes of administration
When the cell product is ready for use, it can be administered in several ways, depending on the purpose of therapy, the disease, and the patient’s condition:
- IV drip
- Intramuscularly
- Intrathecal (spinal tap)
- Retrobulbar (in the eye area)
- Locally (cutaneous covering, joint, cavernous bodies of the penis, etc.)
Usually, the procedure of cell product introduction takes very little time. For example, intravenous infusion takes about 30 minutes. For 2 hours after administration, the patient is monitored (pulse, blood pressure, heart rate, BH, diuresis, ECG, O2 saturation). In the case of complaints, deterioration, or the emergence of new clinical symptoms the patient continues treatment in the hospital until he or she feels well.
In General, the treatment procedure can be carried out within 1 day (subject to the use of SVF or allogeneic cells).
What are the indications, contraindications and side effects of stem cell treatment?
Treatment with cell products is usually appealed in cases where the standard therapy of the underlying disease is not adequately effective or is associated with complications.
Before therapy, it is necessary to exclude contraindications for cell treatment, including:
- Previous bad experience with cell products;
- Any acute infectious disease;
- Cancer or a precancerous condition;
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack in the last 3 months;
- Deviations of some indicators in blood tests;
- Mental disorders and addictions;
- Contraindications to anesthesia and/or high risk of bleeding and/or pathological processes in the area of the proposed biopsy (does not exclude the possibility of using donor cell products);
- Pregnancy and lactation, and some others.
Along with the expected improvements in cell therapy, unwanted side effects are possible. Mesenchymal stromal cell transplantation may rarely cause infusion-related adverse effects (embolic phenomena, allergic reactions, aseptic meningitis with spinal tap administration), infections, or the formation of abnormal tissue. This happens very rarely, but we have to take into account all known risks. In a majority of cases, it is possible to decline the manifestations of the disease, weaken pain symptoms, and correct the function that was affected. The therapies generally improve the standard of living.
Stem cell treatment. Rehabilitation therapy
It is important to understand that in order to achieve the best results, an integrated approach is used, where the use of stem cells is only one of the stages. Complex therapy includes various methods that help stem cells during recovery, for example, physiotherapy, reflexotherapy, ultraviolet or laser blood irradiation, oxygen therapy, and other methods.
The medical advisor of our clinic will tell you if cell-based therapy products can work in your case. For more information, you can contact us online or request a callback from our specialist.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to learn about the expected results of stem cell therapy for your case, what is the cost of the treatment, and its duration.